
Incoterms CIF - Cost, Insurance and Freight
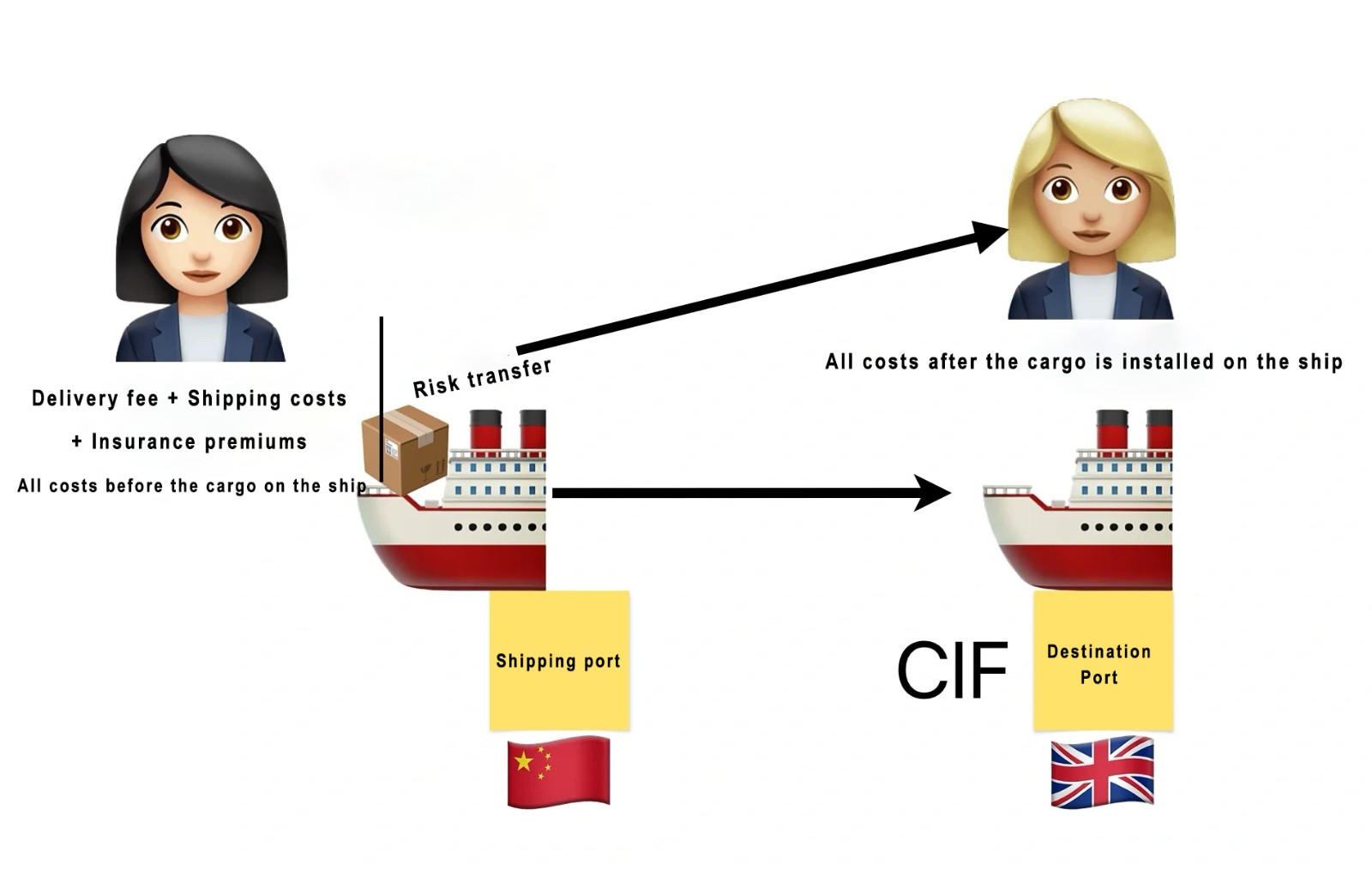
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) is an international trade term defined by Incoterms. It is widely used in global shipping and trade to specify the responsibilities and obligations of the buyer and seller in a sales contract. CIF is applicable when the seller delivers the goods to a carrier at the named port of exportation.
Key Aspects of CIF term
1. Cost of the Goods: The seller bears all costs and risks associated with the goods until they are loaded onto the carrier at the named port of exportation. This includes costs like manufacturing, packaging, and transporting the goods to the port.
2. Insurance: The seller is responsible for obtaining insurance for the goods against loss or damage during the transportation process. The seller must obtain insurance coverage that is at least equal to the contract value of the goods, and this coverage should extend until the goods are unloaded at the named port of destination.
3. Freight Costs: The seller is responsible for paying the freight costs to transport the goods to the named port of destination. Once the goods are loaded onto the carrier, the risk of loss or damage passes to the buyer.
4. Import Procedures: The buyer is responsible for clearing the goods for import and paying any import duties or taxes. The seller must provide the buyer with the necessary documents to facilitate this process, such as the bill of lading and insurance documents.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CIF
Advantages for the Buyer:
The buyer has more control over the transportation of the goods since they are responsible for arranging shipping.
● The buyer can choose their preferred carrier and shipping method.
Advantages for the Seller:
● The seller can more accurately calculate their costs since they control the export process.
● The seller is relieved of the responsibility of arranging shipping and dealing with import procedures.
Disadvantages for the Buyer:
● The buyer bears the risk of loss or damage to the goods once they are loaded onto the carrier.
● The buyer is responsible for dealing with import procedures and paying any associated costs.
Disadvantages for the Seller:
● The seller has less control over the overall transaction since they do not arrange shipping or handle import procedures.
● If the buyer chooses a carrier that is not reliable or experienced, it could delay the delivery of the goods or result in additional costs for the seller.

Conclusion
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) is a common Incoterms trade term used in international trade transactions. It specifies the responsibilities and obligations of the buyer and seller in regard to the cost of the goods, insurance, freight costs, and import procedures. Understanding CIF is essential for businesses engaged in global trade to ensure smooth and efficient transactions.

Incoterms CIF - Cost, Insurance and Freight
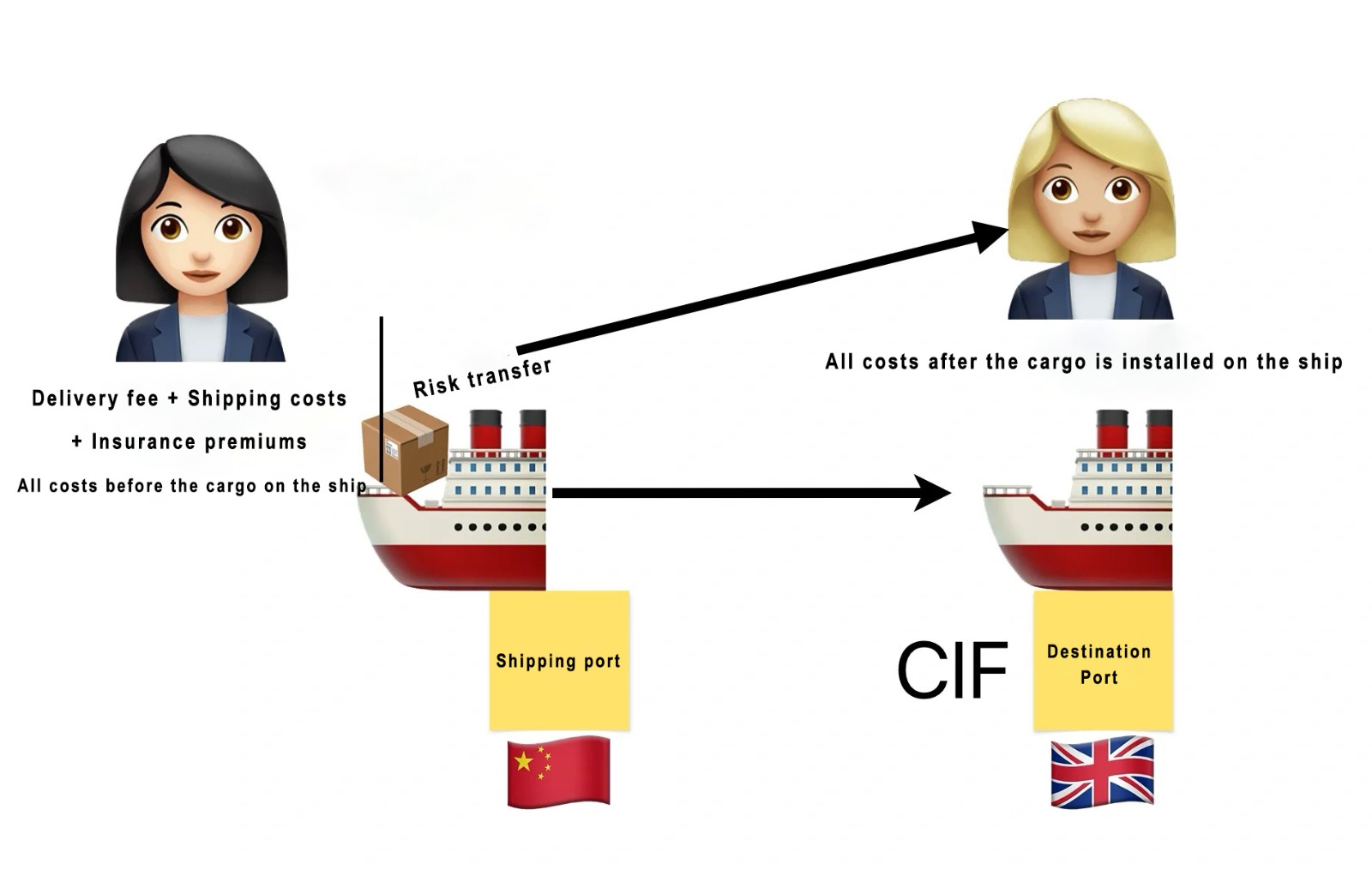
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) is an international trade term defined by Incoterms. It is widely used in global shipping and trade to specify the responsibilities and obligations of the buyer and seller in a sales contract. CIF is applicable when the seller delivers the goods to a carrier at the named port of exportation.
Key Aspects of CIF term
1. Cost of the Goods: The seller bears all costs and risks associated with the goods until they are loaded onto the carrier at the named port of exportation. This includes costs like manufacturing, packaging, and transporting the goods to the port.
2. Insurance: The seller is responsible for obtaining insurance for the goods against loss or damage during the transportation process. The seller must obtain insurance coverage that is at least equal to the contract value of the goods, and this coverage should extend until the goods are unloaded at the named port of destination.
3. Freight Costs: The seller is responsible for paying the freight costs to transport the goods to the named port of destination. Once the goods are loaded onto the carrier, the risk of loss or damage passes to the buyer.
4. Import Procedures: The buyer is responsible for clearing the goods for import and paying any import duties or taxes. The seller must provide the buyer with the necessary documents to facilitate this process, such as the bill of lading and insurance documents.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CIF
Advantages for the Buyer:
The buyer has more control over the transportation of the goods since they are responsible for arranging shipping.
● The buyer can choose their preferred carrier and shipping method.
Advantages for the Seller:
● The seller can more accurately calculate their costs since they control the export process.
● The seller is relieved of the responsibility of arranging shipping and dealing with import procedures.
Disadvantages for the Buyer:
● The buyer bears the risk of loss or damage to the goods once they are loaded onto the carrier.
● The buyer is responsible for dealing with import procedures and paying any associated costs.
Disadvantages for the Seller:
● The seller has less control over the overall transaction since they do not arrange shipping or handle import procedures.
● If the buyer chooses a carrier that is not reliable or experienced, it could delay the delivery of the goods or result in additional costs for the seller.

Conclusion
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) is a common Incoterms trade term used in international trade transactions. It specifies the responsibilities and obligations of the buyer and seller in regard to the cost of the goods, insurance, freight costs, and import procedures. Understanding CIF is essential for businesses engaged in global trade to ensure smooth and efficient transactions.
Popular Articles





Categories
Share
The latest blogs and insights on what is happening in international transport and logistics.